Prosthesis Overview
A prosthesis is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part lost due to trauma, disease, or congenital conditions.
It restores function, appearance, and enhances mobility and independence.
Restoring mobility, independence, and confidence through advanced prosthetic solutions
Schedule a ConsultationA prosthesis is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part lost due to trauma, disease, or congenital conditions.
It restores function, appearance, and enhances mobility and independence.

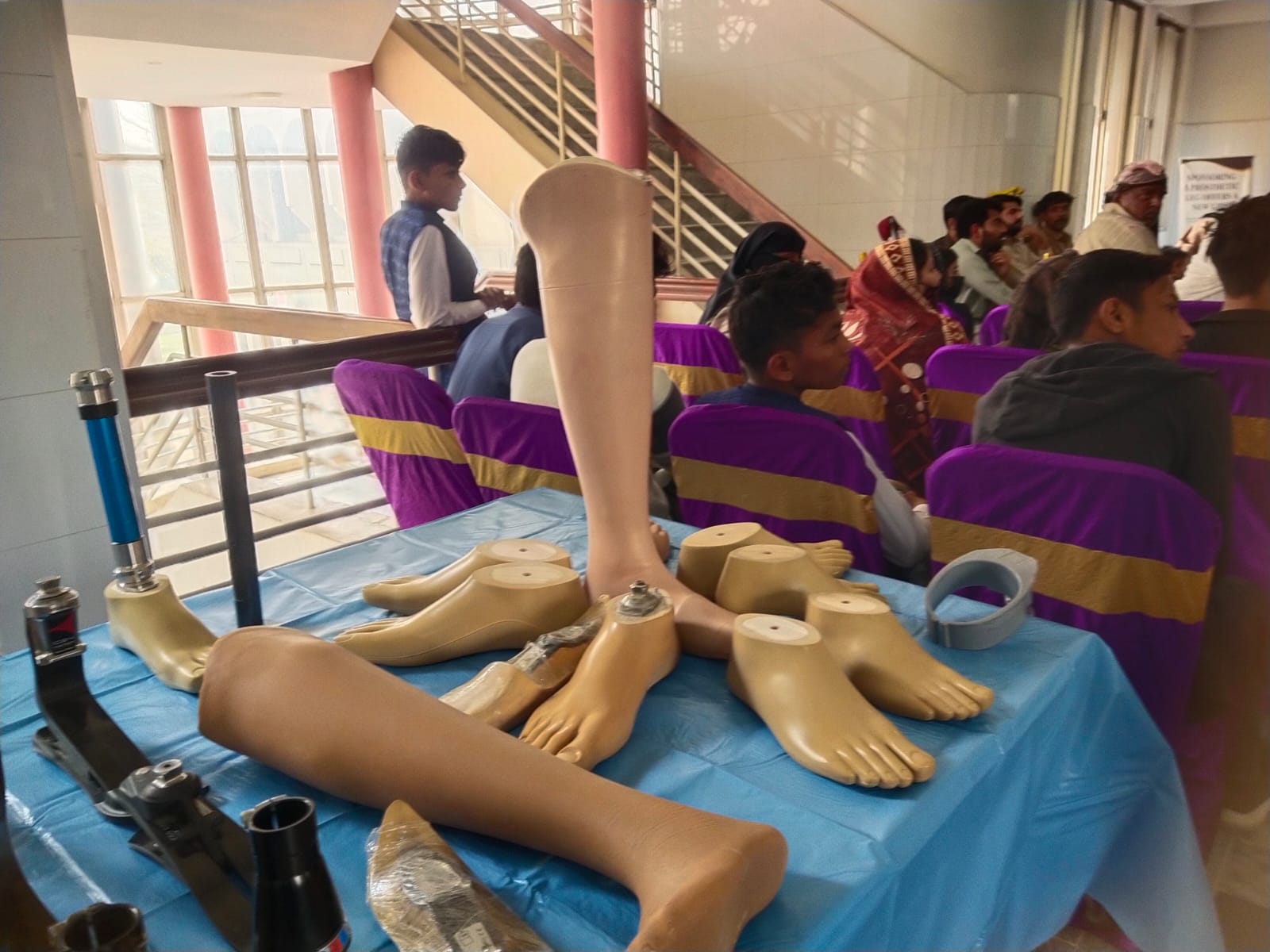
Designed for leg amputations to restore walking ability and mobility:

Custom-designed prosthetic legs that restore natural gait and mobility.
Designed for arm and hand amputations to restore function and dexterity:

Advanced prosthetic arms and hands that restore function and appearance.
Prostheses are attached to the residual limb using custom sockets and suspension systems for secure fit.
Controlled by body power (muscle movement) or external power (battery-powered, myoelectric systems).
Customized for specific activities like walking, running, climbing, or specialized tasks.
Modern prosthetics incorporate advanced materials like carbon fiber, silicone, and microprocessor-controlled joints that adapt to different walking speeds and terrains.
Custom-made interface that fits onto the residual limb for comfort and stability.
Secures the prosthesis to the body using straps, suction, or pin-lock mechanisms.
Mechanical or microprocessor-controlled knees, ankles, elbows, or wrists.
Structural connector that provides support and determines prosthesis length.
Enables movement and function - prosthetic feet, hands, or specialized tools.
Cushioning layer (gel liners, socks) between the socket and residual limb.
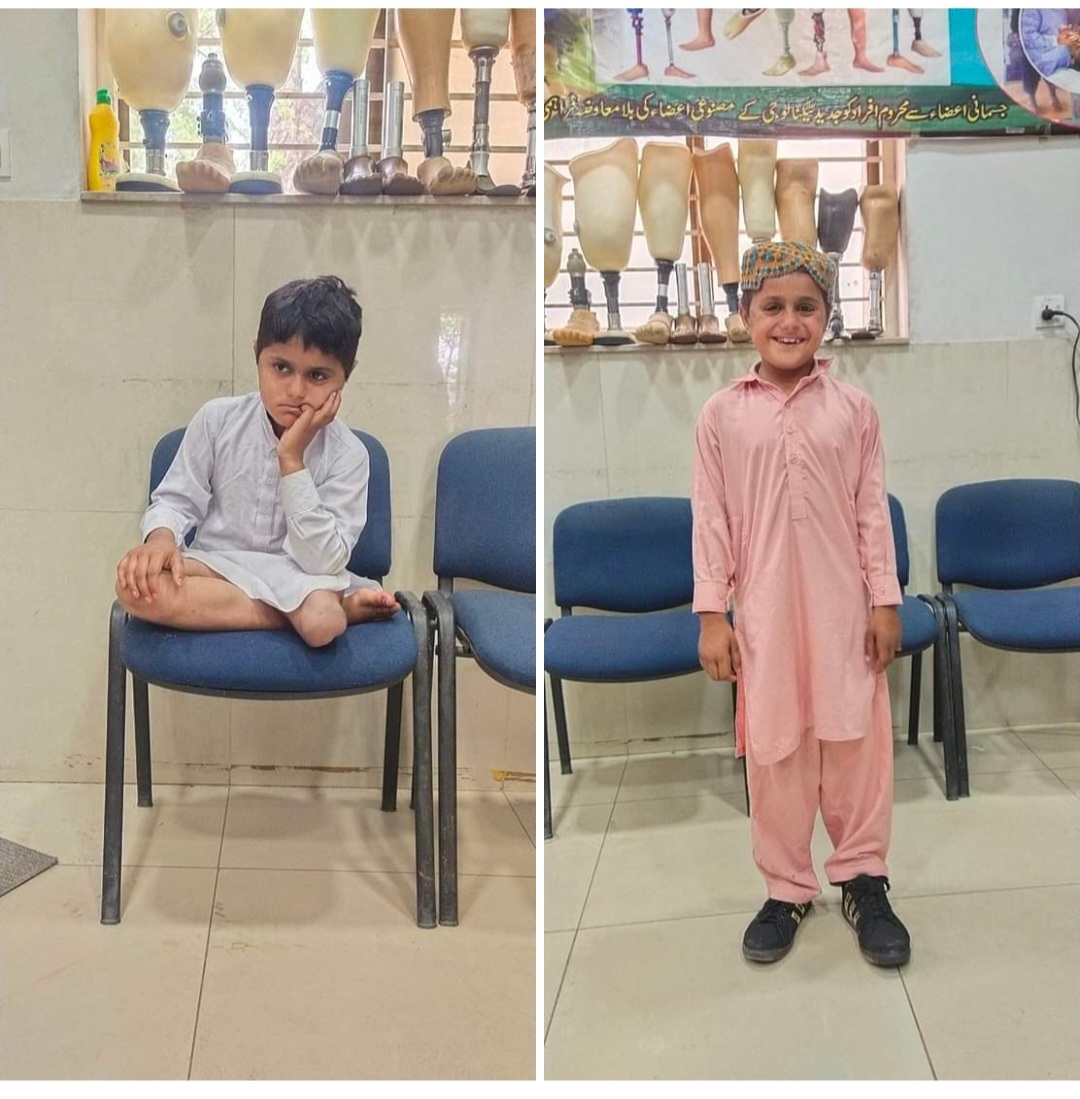
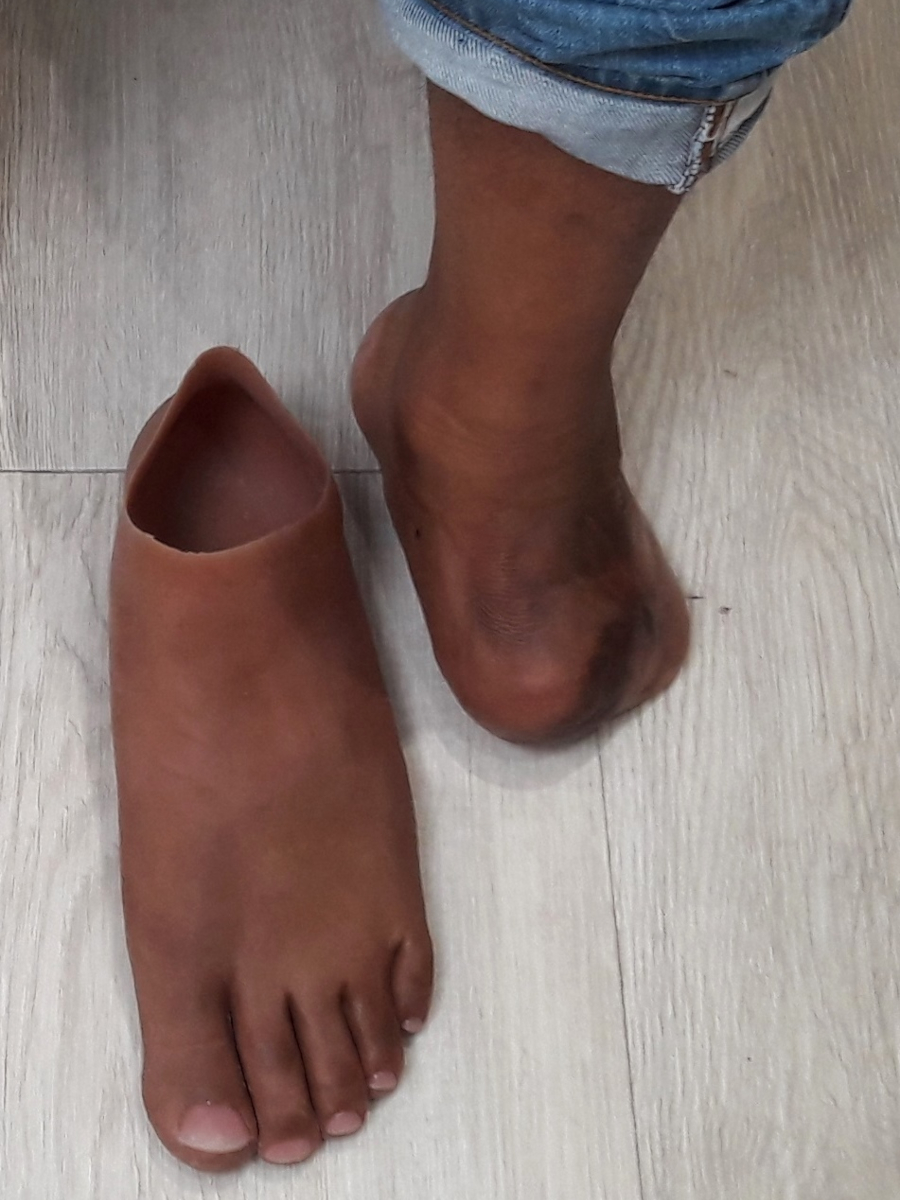
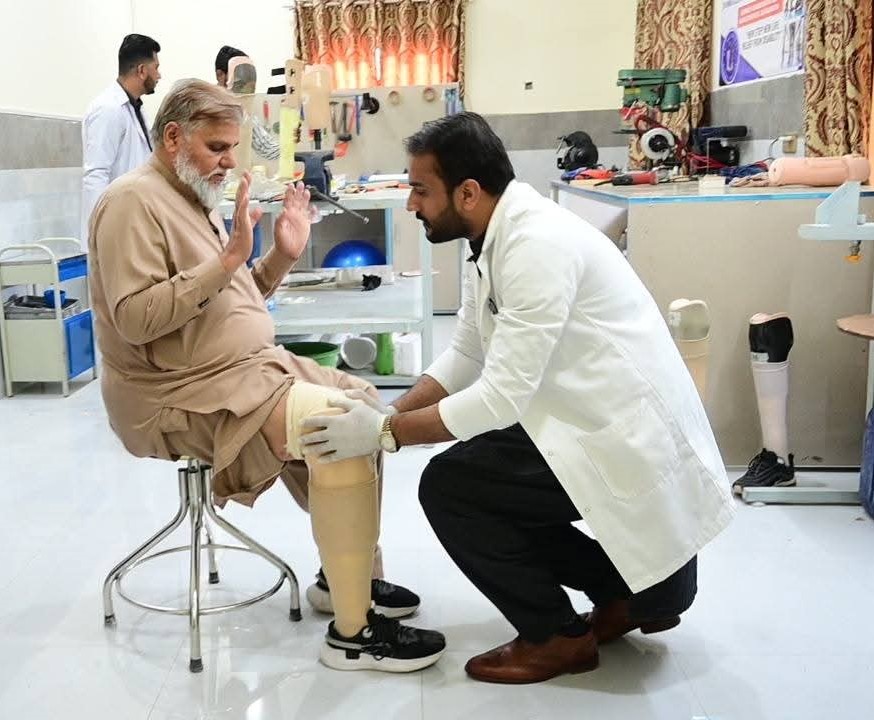



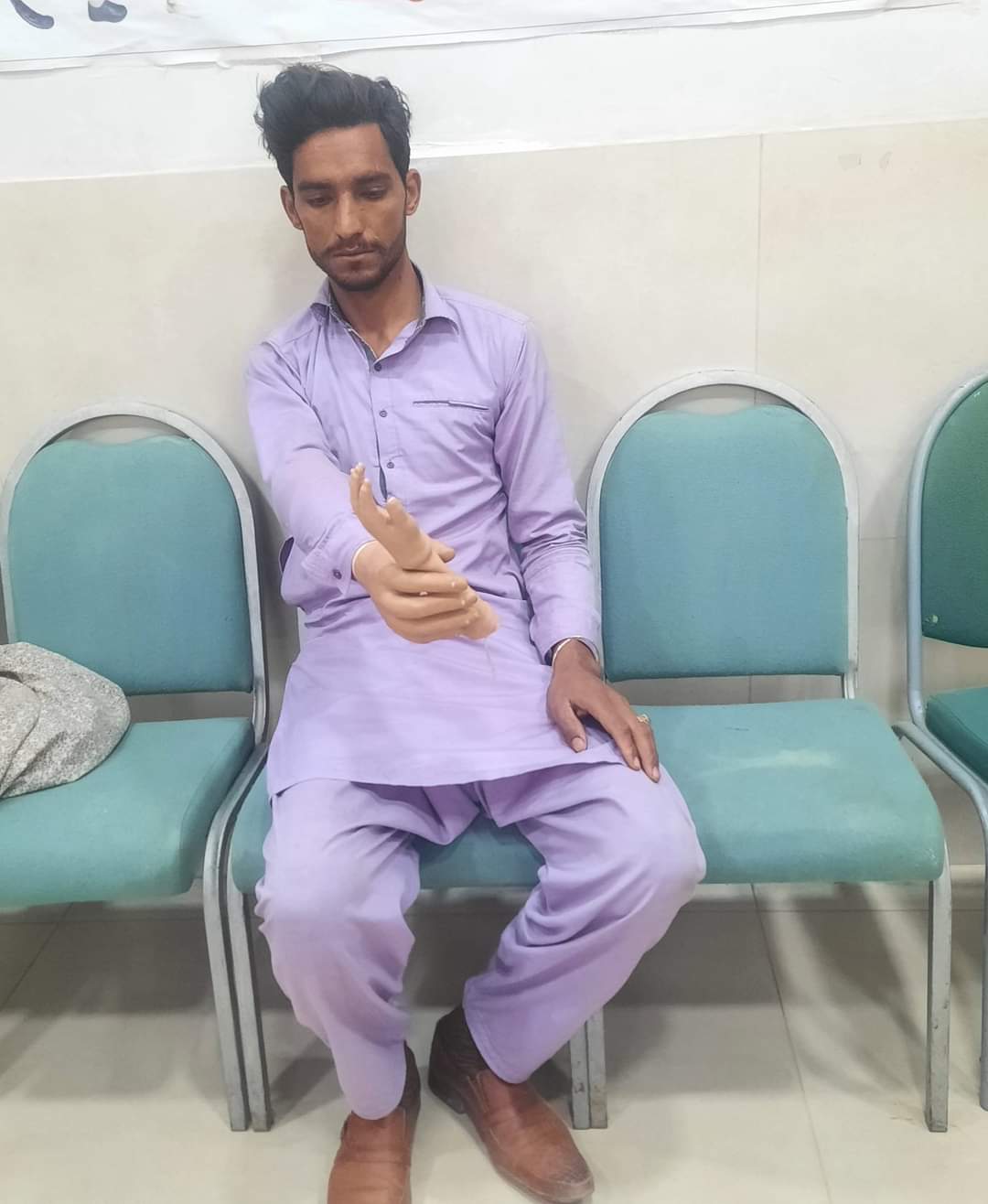
Close collaboration between physiotherapists and prosthetists is essential for successful rehabilitation.
Therapists should understand:
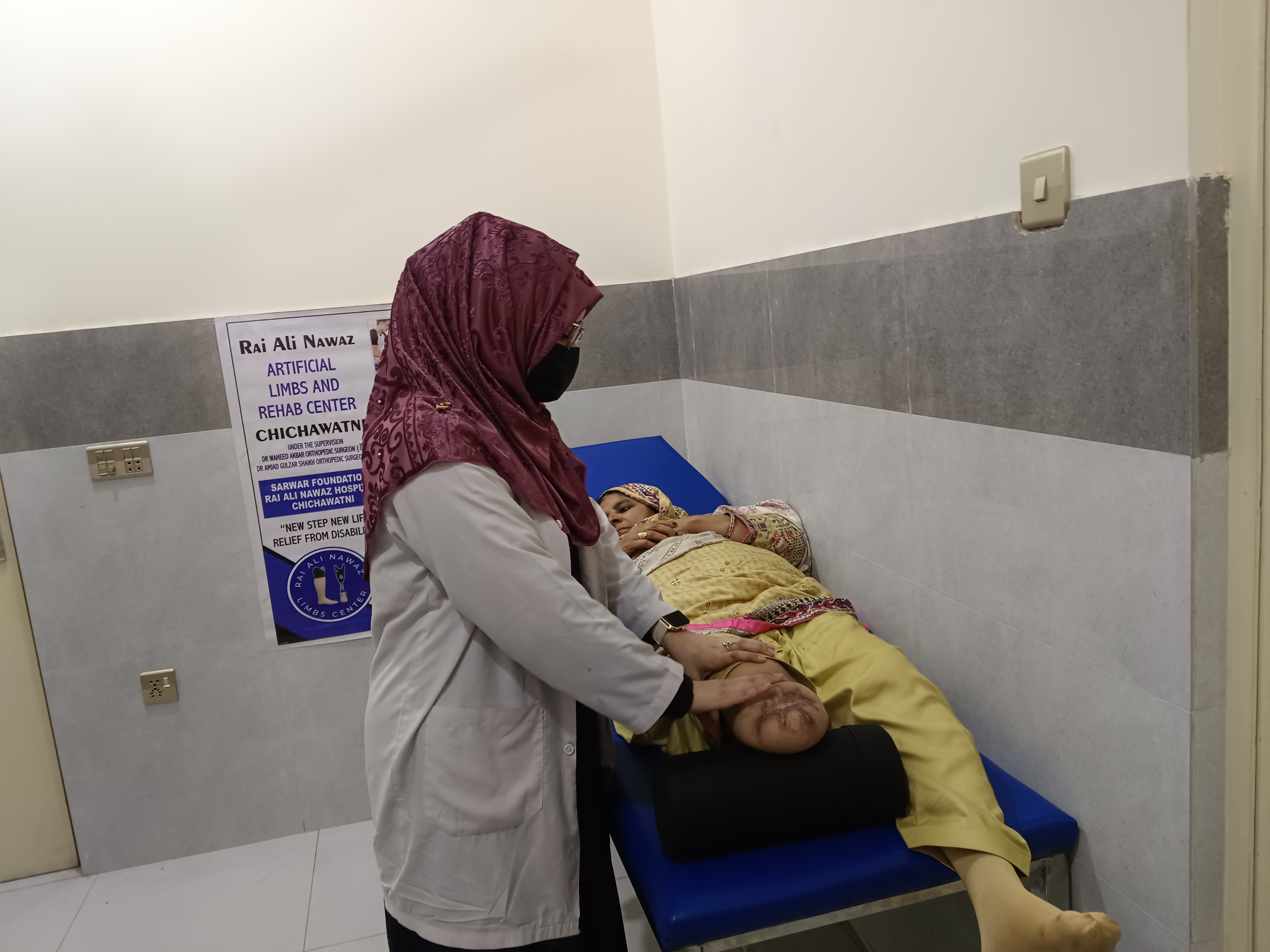
Our integrated approach combines prosthetic fitting with physiotherapy to ensure optimal outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Our team of specialists is ready to help you regain independence and improve your quality of life